Understanding Unhandled Flow Faults
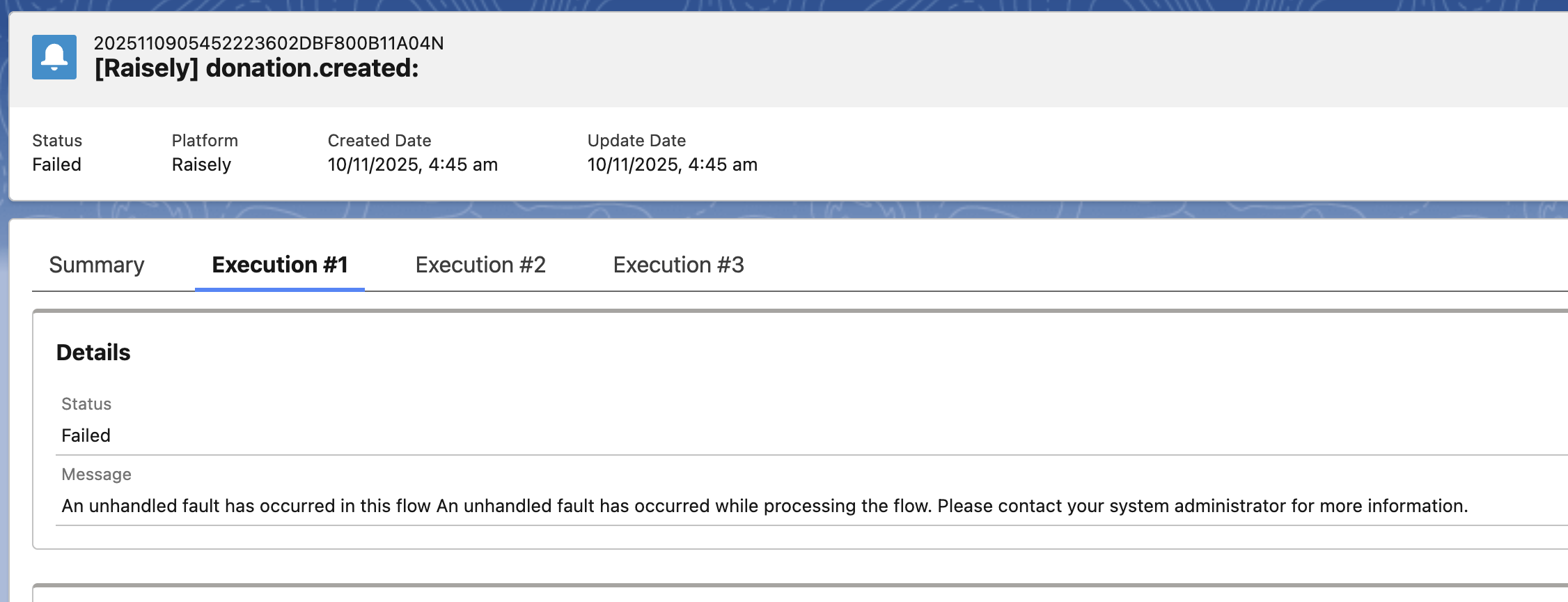
The error message "An unhandled fault has occurred in this flow" indicates that a Salesforce Lightning Flow encountered an unexpected exception during execution that was not captured by the flow's error handling logic. This is a generic Salesforce system error that occurs when a flow encounters a problem it cannot resolve on its own, such as validation rule failures, required field violations, duplicate value conflicts, permission issues, or business logic issues.
Identifying the Failing Flow
.png)
To troubleshoot this error when it occurs during MoveData notification processing, navigate to the failed notification in the MoveData Notifications interface and access the Execution tab to view the detailed execution log. The execution log provides a chronological timeline of each processing stage, allowing you to identify exactly where the failure occurred. The log will tell you which flow was executing, where failure is taking place.
Viewing the Failed Flow
.png)
Once the failing flow has been identified, its error can be traced using the "Paused and Failed Flow Interviews" functionality. Navigate to Setup and search for "Paused and Failed Flow Interviews" in the Quick Find box. This Salesforce feature captures failed flow executions and provides specific error details not available in the generic error message, including the exact element where the failure occurred, the specific error text, and the variable values at the time of failure. The list often appears empty by default, so toggle the view filter to show failed interviews rather than paused ones.
Click on a failed interview to open the detailed failure view, which presents the flow as a visual diagram with the failed element clearly highlighted. The interface displays the error message alongside the specific element that caused the failure, making it straightforward to pinpoint problematic decision nodes, record operations, or assignments. You can also inspect the input and output variables for each element in the execution path, allowing you to trace exactly how data flowed through the flow before the failure occurred. This visual approach is particularly useful for complex flows with multiple branches, as it immediately shows which path was taken and where processing stopped.
Common Failure Reasons
| Error | Description |
|---|---|
FIELD_CUSTOM_VALIDATION_EXCEPTION | This occurs when a record fails to save because it violates a custom validation rule defined on the object, ie. You must specify either an Account or a Contact. |
LIMIT_EXCEEDED: System.LimitException: Too many SOQL queries: 101 | This error occurs when the execution of a notification exceeds Salesforce's governor limit of 100 SOQL database queries, typically caused by workflows or triggers outside of MoveData. See too-many-soql-queries-101.md |
CANNOT_EXECUTE_FLOW_TRIGGER | This error occurs when a record-triggered flow fails to execute, typically due to the flow being deactivated, deleted, or containing configuration errors that prevent it from running when its trigger conditions are met. |
UNABLE_TO_LOCK_ROW | This occurs when a record cannot be updated because another transaction is simultaneously attempting to modify the same record. MoveData will retry 3 times before a notification is marked a failure; this error is usually overcome with the second automatic retry, often making this error misleading. |
CANNOT_INSERT_UPDATE_ACTIVATE_ENTITY | This error occurs when an operation fails due to an issue in a related automation such as a trigger, workflow rule, or process builder that fires during the record save or update. The specific cause detailed in the accompanying error message. This is often indicates there is an issue with the Salesforce NPSP. |
Apex CPU time limit exceeded | This error occurs when a transaction exceeds Salesforce's 10-second limit for synchronous processing, typically caused by complex logic, inefficient loops, or excessive automation chains consuming too much computational time. See apex-cpu-time-limit-exceeded.md |
INSUFFICIENT_ACCESS_ON_CROSS_REFERENCE_ENTITY | This occurs when a user attempts to create or update a record that references another record by ID (such as a lookup) to which doesn't exist or which they do not have sufficient access permissions. |
Advanced: Using Salesforce Debug Logs
If the built-in execution logs do not provide sufficient detail, Salesforce's native debug logs can be enabled for the MoveData authorised user to capture the full Apex execution context. These logs operate at a very detailed level and are often used when debugging at a higher level has failed.